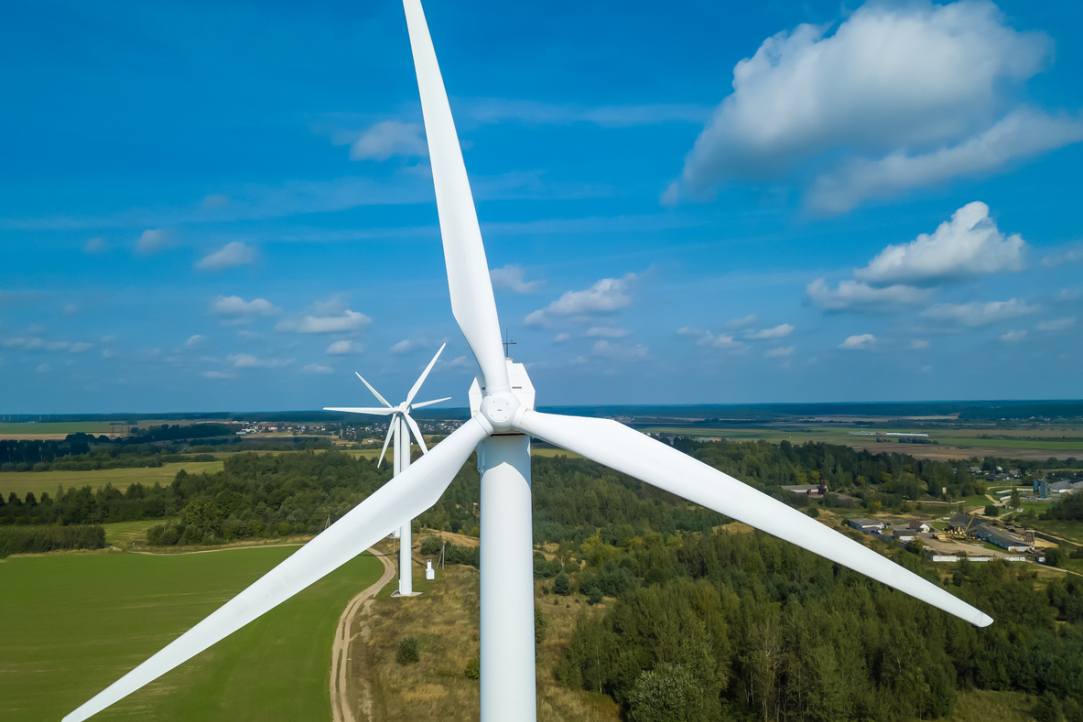
Green Energy Patents Boost Company Profitability

For nuclear energy, the increase can be up to 1.6%
An ESG strategy—Environmental, Social, and Corporate Governance—not only helps preserve the environment but can also generate tangible income. Thus, the use of renewable energy sources (RES) and green technologies in the energy sector enhances return on investment and profitability. In contrast, higher CO2 emissions result in lower financial performance. This has been demonstrated in a collaborative study by the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences and the European University at St. Petersburg. Their findings have been published in Frontiers in Environmental Science.
In recent years, green energy technologies have made significant advancements. Governments and businesses invest hundreds of billions of dollars in developing renewable energy sources (RES), nuclear energy, and electric transportation. In 2020, their share accounted for 40% of all investments in the energy sector, totalling $400 billion. In the European Union, spending on green energy is 3.5 times higher than on traditional energy. Meanwhile, China has reduced investments in the gas and oil sectors by 40% to focus on developing RES. Increasingly, research demonstrates that adopting green technologies can have a positive impact on company profitability.
Elena Makeeva, Associate Professor at the HSE Faculty of Economics, Konstantin Popov, Research Assistant at the HSE Corporate Finance Centre, and Olga Teplova, Research Fellow at the European University at St. Petersburg, have investigated how investments in green energy impact the profitability of energy companies in the BRICS countries. The researchers studied 63 largest firms in the BRICS countries and examined their key financial performance indicators, including return on assets (ROA), return on invested capital (ROIC), and market capitalisation.
CO2 emissions and patents related to three primary types of green energy—renewable energy technologies, combustion technologies with mitigation potential, and nuclear energy technologies—were considered as independent variables. China leads among BRICS member countries in all types of patents, with its share reaching 94% for patents in the field of renewable energy and 89% for patents related to hybrid energy systems.

The model also incorporated the company's revenue and investments, along with the per capita GDP of the company's home country, as controls. The authors constructed several models to establish a connection between investments in green technologies, carbon dioxide emissions, and the return on assets and investments, and market capitalisation of companies.
They have found that higher CO2 emissions significantly reduce company profitability and negatively affect market capitalisation: a 1% increase in carbon dioxide emissions results in nearly a 2% decrease in company profitability. The return on investment decreases even further, by 5% to 7%, along with a decrease in market capitalisation. Conversely, the more 'green energy' patents a company registers, the greater its profitability. The return on assets increases by 0.7% on average, and patents in the field of nuclear energy result in the largest increase of up to 1.6%. The return on investment has been found to increase by 2% to 3%. The researchers note that patents for renewable energy technologies contribute significantly only to ROIC, whereas combustion technologies with mitigation potential and nuclear technologies positively influence all financial performance indicators of companies. The authors also advocate for further advancements in nuclear power technology, since a nuclear power plant is a powerful, stable, and low carbon energy source with a long operational lifespan.
However, it should be noted that investments in green energy typically involve long-term commitments and do not yield immediate financial returns. This study demonstrates that businesses prioritising social and environmental responsibility in their operations can eventually achieve significant profits.

Associate Professor, Faculty of Economics, HSE University
The development of green energy should be a priority for BRICS countries, and investing in infrastructure and improving legislation are crucial factors for an expansion of low-carbon technologies in the electric power industry.
See also:
HSE University Develops Tool for Assessing Text Complexity in Low-Resource Languages
Researchers at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain have developed a tool for assessing text complexity in low-resource languages. The first version supports several of Russia’s minority languages, including Adyghe, Bashkir, Buryat, Tatar, Ossetian, and Udmurt. This is the first tool of its kind designed specifically for these languages, taking into account their unique morphological and lexical features.
HSE Scientists Uncover How Authoritativeness Shapes Trust
Researchers at the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience have studied how the brain responds to audio deepfakes—realistic fake speech recordings created using AI. The study shows that people tend to trust the current opinion of an authoritative speaker even when new statements contradict the speaker’s previous position. This effect also occurs when the statement conflicts with the listener’s internal attitudes. The research has been published in the journal NeuroImage.
Language Mapping in the Operating Room: HSE Neurolinguists Assist Surgeons in Complex Brain Surgery
Researchers from the HSE Center for Language and Brain took part in brain surgery on a patient who had been seriously wounded in the SMO. A shell fragment approximately five centimetres long entered through the eye socket, penetrated the cranial cavity, and became lodged in the brain, piercing the temporal lobe responsible for language. Surgeons at the Burdenko Main Military Clinical Hospital removed the foreign object while the patient remained conscious. During the operation, neurolinguists conducted language tests to ensure that language function was preserved.
AI Overestimates How Smart People Are, According to HSE Economists
Scientists at HSE University have found that current AI models, including ChatGPT and Claude, tend to overestimate the rationality of their human opponents—whether first-year undergraduate students or experienced scientists—in strategic thinking games, such as the Keynesian beauty contest. While these models attempt to predict human behaviour, they often end up playing 'too smart' and losing because they assume a higher level of logic in people than is actually present. The study has been published in the Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization.
Scientists Discover One of the Longest-Lasting Cases of COVID-19
An international team, including researchers from HSE University, examined an unusual SARS-CoV-2 sample obtained from an HIV-positive patient. Genetic analysis revealed multiple mutations and showed that the virus had been evolving inside the patient’s body for two years. This finding supports the theory that the virus can persist in individuals for years, gradually accumulate mutations, and eventually spill back into the population. The study's findings have been published in Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.
HSE Scientists Use MEG for Precise Language Mapping in the Brain
Scientists at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain have demonstrated a more accurate way to identify the boundaries of language regions in the brain. They used magnetoencephalography (MEG) together with a sentence-completion task, which activates language areas and reveals their functioning in real time. This approach can help clinicians plan surgeries more effectively and improve diagnostic accuracy in cases where fMRI is not the optimal method. The study has been published in the European Journal of Neuroscience.
For the First Time, Linguists Describe the History of Russian Sign Language Interpreter Training
A team of researchers from Russia and the United Kingdom has, for the first time, provided a detailed account of the emergence and evolution of the Russian Sign Language (RSL) interpreter training system. This large-scale study spans from the 19th century to the present day, revealing both the achievements and challenges faced by the professional community. Results have been published in The Routledge Handbook of Sign Language Translation and Interpreting.
HSE Scientists Develop DeepGQ: AI-based 'Google Maps' for G-Quadruplexes
Researchers at the HSE AI Research Centre have developed an AI model that opens up new possibilities for the diagnosis and treatment of serious diseases, including brain cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. Using artificial intelligence, the team studied G-quadruplexes—structures that play a crucial role in cellular function and in the development of organs and tissues. The findings have been published in Scientific Reports.
New Catalyst Maintains Effectiveness for 12 Hours
An international team including researchers from HSE MIEM has developed a catalyst that enables fast and low-cost hydrogen production from water. To achieve this, the scientists synthesised nanoparticles of a complex oxide containing six metals and anchored them onto various substrates. The catalyst supported on reduced graphene layers proved to be nearly three times more efficient than the same oxide without a substrate. This development could significantly reduce the cost of hydrogen production and accelerate the transition to green energy. The study has been published in ACS Applied Energy Materials. The work was carried out under a grant from the Russian Science Foundation.
HSE Researchers Offer Guidance to Prevent Undergraduate Burnout
Researchers at the HSE Institute of Education have identified how much time students should ideally devote to their studies, extracurricular activities, and personal life to maintain strong academic performance without compromising their mental health. An analysis of responses from 2,753 students, combined with their actual academic results, revealed several risk factors—such as excessive homework—as well as positive factors, including sufficient sleep, regular exercise, and moderate participation in projects. Based on these findings, the researchers developed practical recommendations for both students and universities. The paper has been published in the European Journal of Education.