Biologists at HSE University Warn of Potential Errors in MicroRNA Overexpression Method
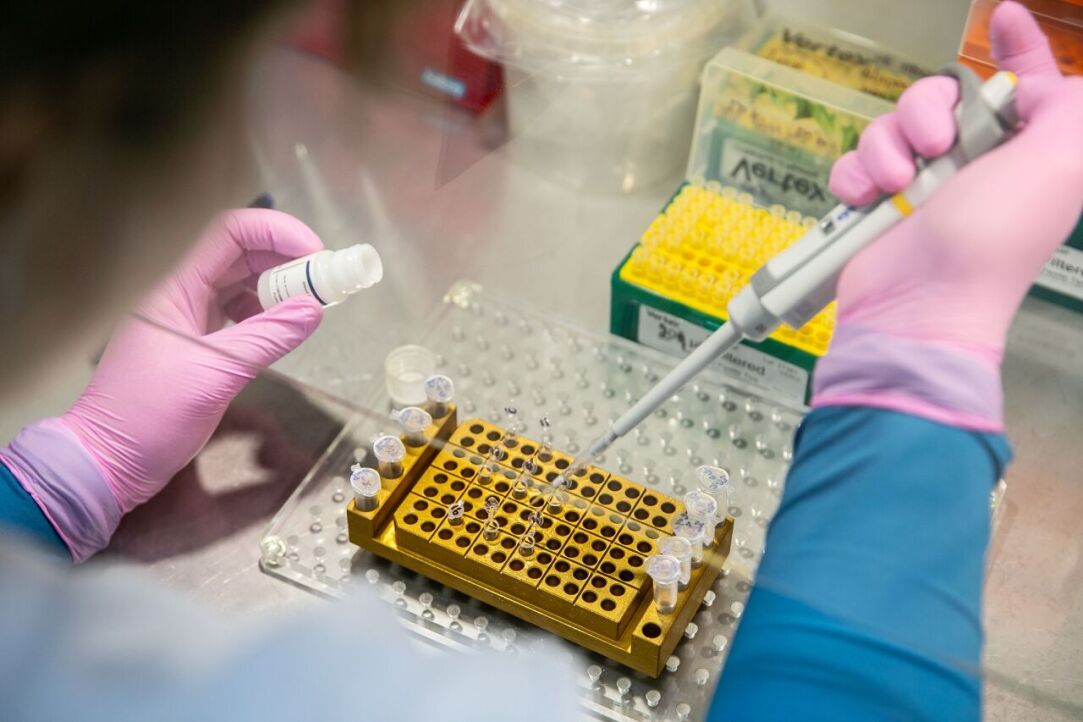
Researchers at HSE University and the RAS Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry have discovered that a common method of studying genes, which relies on the overexpression of microRNAs, can produce inaccurate results. This method is widely used in the study of various pathologies, in particular cancers. Errors in experiments can lead to incorrect conclusions, affecting the diagnosis and treatment of the disease. The study findings have been published in BBA.

Neuroscientists from HSE University Learn to Predict Human Behaviour by Their Facial Expressions
Researchers at the Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience at HSE University are using automatic emotion recognition technologies to study charitable behaviour. In an experiment, scientists presented 45 participants with photographs of dogs in need and invited them to make donations to support these animals. Emotional reactions to the images were determined through facial activity using the FaceReader program. It turned out that the stronger the participants felt sadness and anger, the more money they were willing to donate to charity funds, regardless of their personal financial well-being. The study was published in the journal Heliyon.

Physicists from Russia and Brazil Unveil Mystery behind Complex Superconductor Patterns
Scientists at HSE MIEM and MIPT have demonstrated that highly complex spatial structures, similar to the intricate patterns found in nature, can emerge in superconductors. Mathematically, these patterns are described using the Ginzburg–Landau equation at a specific combination of parameters known as the Bogomolny point. The paper has been published in the Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter.

Adhesive Tape Helps Create Innovative THz Photodetector
An international team of researchers, including scientists at HSE University and Moscow Pedagogical State University (MPGU), has developed a novel photodetector composed of a thin superconducting film, capable of detecting weak terahertz (THz) radiation. This discovery holds promise for studying objects in space, developing wireless broadband communication systems, and making advancements in spectroscopy. The study has been published in Nano Letters.

Operation of Cellular Networks Found Similar to Bacteria Growth in Petri Dish
Scientists at the HSE Laboratory for Computational Physics have developed a new model for analysing communication networks that can significantly enhance the speed of mobile communications. To achieve this, the researchers used computational physics methods and phase transition models. It turns out that the functioning of cellular networks is in many ways similar to the growth of surfaces in physics. The study was performed using the HPC cHARISMa cluster at HSE University. The study findings have been published in Frontiers in Physics.
%20(1).png)
Research Results from HSE University Form Basis of UN Report on Volunteering
The first Regional State of Volunteering in Central Asia Review was presented at the UN Headquarters in New York as part of the annual High-Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development. The preparation of this document included the research conducted by the HSE Centre for Studies of Civil Society and the Nonprofit Sector (CSCSNS), with Viacheslav Ivanov, the Chief Expert of the Centre, serving as the lead author of the review.

Spelling Sensitivity in Russian Speakers Develops by Early Adolescence
Scientists at the RAS Institute of Higher Nervous Activity and Neurophysiology and HSE University have uncovered how the foundations of literacy develop in the brain. To achieve this, they compared error recognition processes across three age groups: children aged 8 to 10, early adolescents aged 11 to 14, and adults. The experiment revealed that a child's sensitivity to spelling errors first emerges in primary school and continues to develop well into the teenage years, at least until age 14. Before that age, children are less adept at recognising misspelled words compared to older teenagers and adults. The study findings have beenpublished in Scientific Reports .

HSE Researchers Demonstrate Effectiveness of Machine Learning in Forecasting Inflation
Inflation is a key indicator of economic stability, and being able to accurately forecast its levels across regions is crucial for governments, businesses, and households. Tatiana Bukina and Dmitry Kashin at HSE Campus in Perm have found that machine learning techniques outperform traditional econometric models in long-term inflation forecasting. The results of the study focused on several regions in the Privolzhskiy Federal District have been published in HSE Economic Journal.

Ruthenium Complexes Can Accelerate the Development of New Medicines
A group of scientists at INEOS RAS, HSE University, and MIPT have synthesised catalysts containing a ruthenium atom and an aromatic ring. The scientists have isolated the mirror forms of these catalysts and investigated their effectiveness in producing heterocycles, which are commonly found in the structures of drugs. The research findings have been published in Chemical Communications.

Connecting Space and Time: Bilinguals Associate Time with Space in Both Their First and Second Languages
An international team of researchers including scientists at HSE University investigated how bilingual individuals associate time with space. It turns out that in both their first and second languages, people associate the past with the left side of space and the future with the right. In fact, the higher the proficiency in a second language, the more pronounced this relationship becomes. The study findings have been published in Scientific Reports.